Growth and development are inseparable but they differ from each other. Growth represents an individual’s physical changes and development represents an individual’s overall changes, structure, and shape. Growth represents the Quantitative chance while Development represents both Quantitative and Qualitative changes
Knowledge of growth and development at various stages is essential for the teacher. The teacher has to stimulate the growth and development of a child. He can do it only if he has proper knowledge of growth and development at various stages.
Meaning of Growth and Development
Growth terms represent a physical sense of a person, i.e. height, weight, size length etc. Growth is quantitive. It starts with conception but ends at some particular age.
Development implies the overall change in shape, form or structure, along with the function of the organ. Development is both quantitative and qualitative. It is a continuous process starting from the Womb and ending with the tomb.
Principles of Growth and Development
The important principles of growth and development are given below-
1. Principle of Continuity
The development follows the principle of continuity which means that development is a continuous process. It starts with pre-natal and ends with death (womb to tomb).
2. Principle of Integration
Development thus involves a movement from the whole to parts and from parts to the whole and this way it is the integration of the whole and its parts as well as the specific and general responses. It enables a child to develop satisfactorily concerning various aspects or dimensions of his personality.
Example: Child first starts to learn hand movement then finger movement and then learn the movement of both hand and finger together this is called integration
3. Principle of lack of uniformity in the developmental rate
Development through a continuous process, but does not exhibit steadiness and uniformity in terms of the rate of development in various development of personality or the developmental periods and stages of life.
Example: A person may have a high rate of growth and development in terms of height and weight but may not have the same pace of mental and social development.
4. Principle of individual difference
Every organism is a distinct creation in itself. One of the most important principles of development is that involves individual differences. There is no fixed rate of development. That all children will learn to walk is universal, but the time at which each child takes his or her first step may vary.
Example: Some children walk at 10 months while others at 12 months. Every child has a unique rate of growth and development
5. Principle of uniformity pattern
Although development does not proceed at a uniform rate and shows marked individual differences concerning the process and outcome of various stages of development, it follows a definite pattern in one or the other dimension which is uniform and universal concerning the individual of a species.
Example: Crawling, Walking, and Talking are the stages which follow in sequence pattern. Children first learn crawling then walking and then talking
6. Principe of proceeding from general to specific
While developing any aspect of personality. The child first picks up or exhibits a general response and learns how to show specific and goal-directed responses afterwards.
Example: when Children is less than 3 months of age and is shown a rattle, she/he
would get excited and move her arms and kick her legs. This is a general response.
At 5 months of age, she/he would reach out to hold it in her hand. This is a specific
response.
Also Read: Bloom’s Taxonomy-3 Domains of Learning
7. Principle of interaction between Heredity and Environment
The development of a child is a process that cannot be defined wholly based on either heredity or environment. Both have to play an important role in development. There are arguments in favour of both. However, most psychologists agree that an interplay of these two factors leads to development.
Where heredity decides or sets some limits on development ( mostly physical), environmental influences complete the developmental process ( qualitative). Environmental influences provide space for multidimensional development through interaction with family, peers, society, and so on. Growth and development are a joint product of heredity and environment.
8. Principle of interrelation
Various aspects or dimensions of one’s growth and development are interrelated. What is achieved or not achieved in one or other dimensions in the course of the gradual and continuous process of development surely affects the development of other dimensions.
A healthy body tends to develop a healthy mind and an emotionally stable, physically strong, and socially conscious personality. Inadequate physical or mental development may, on the other hand, result in a socially or emotionally maladjusted personality.
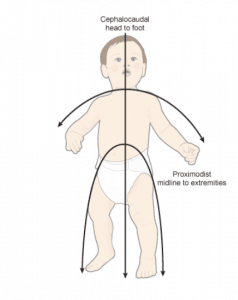
9. Principle of Cephalocaudal
Development proceeds in the direction of the longitudinal axis. Development from head to foot or toe. That is why, before it becomes able to stand, the child first gains control over his head and arms and then over his legs.
10. Principle of Proximodistal
Development of motor skills to start at central body parts to outwards. That is why, in the beginning, the child is seen to exercise control over the large fundamental muscles of the arm and then hand and only afterwards over the smaller muscles of the fingers.
11. Principle of predictability
Development is predictable, which means that with the help of the uniformity of pattern and sequence of development. We can go to a great extent, forecast the general nature and behavior of a child in one or more aspects or dimensions at any particular stage of its growth and development. We can know the particular age at which children will learn to walk, speak, and so on.
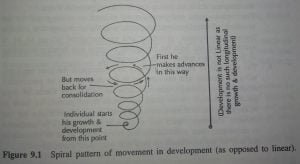
12. Principle of Spiral versus Linear advancement
The child doesn’t proceed straight or linear on the path of development at any stage never takes place at a constant or steady pace. After the child had developed to a certain level, there is likely to be a period of rest for consolidation of the developmental progress achieved till then. In advancing further, therefore, the development turns back and then moves forward again in a spiral pattern
13. Principle of Association of Maturation and Learning
Biological growth and development are known as maturation. Biological changes involve changes in the brain and the nervous system, which provide new abilities to a child. Development proceeds from simple to complex. In the beginning, a child learns through concrete objects and gradually moves to abstract thinking. This transition happens because of the maturation
Conclusion
The principle of growth and development is one of the most important topics in child development psychology. We as a teacher must understand the different stages and principles of growth and development so that we can teach the students according to their age, interests, skills, and needs
Educational Implication of the Principles of Growth and Development
The knowledge of the above–mentioned principles of growth and development may prove beneficial to us in several ways described below:
- Development is a continuous and non-stop process at all periods and stages of human life. Therefore, we should never give up our efforts to achieve perfection in terms of development in the different dimensions of our personalities.
- The principle of individual differences among children reminds us to understand the wide individual differences at all periods of growth and development. Each child should be helped along the developmental; process according to their ability, strengths, and limitations.
- The principles related to growth and development suggest a pattern or trend for the advancement of children on the developmental path. This knowledge can help us to understand as what is often expected in terms of the right growth and development at a specific developmental stage and we can then plan accordingly to achieve it by organizing the environmental experiences.
- The principles of proceeding from general to specific responses and the principles of integration help us to develop appropriate learning experiences to achieve maximum growth and development.
- Principles of interrelation and interdependence direct us to make every effort from the very beginning for the all-around harmonious development of the personalities of our child and caution us no to encourage the development of particular aspects at the cost of another.
- The principles of spiral advancement of development help us to make adequate arrangements for subsequent progress and consolidation of the progress achieved during specific developmental stages.
- The cephalocaudal and proximodistal tendencies as suggested by the principle of developmental direction help us to arrange suitable learning experiences, processes, and environmental set-ups to accommodate and help the children to grow and develop according to the trend and nature of these tendencies.
- The principle of interaction reminds us to recognize the joint responsibilities of heredity and environment in the development of personality. Genetic makeup is inborn and influences a limited amount of development, so we can provide a suitable environment for children to take out their maximum growth and development.
References:
- Mangal, S. (2007). Advanced Educational Psychology (2nd ed., pp. 99-101). New Delhi: Prentice-Hall of India private limited.
- Kumar, S. (2019). Child Development and pedagogy (5th ed., pp. 7-8). Noida: Pearson India Education Pvt, Ltd.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the orthogenetic principles of development?
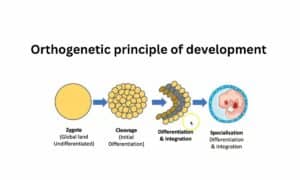
The orthogenetic principle of development suggests that development proceeds from Global and undifferentiated states to states of increasing differentiation, integration, and hierarchical integration
what are the principles of growth and development in psychology?
The psychological principles of growth and development cover the physical, cognitive, and socioemotional growth of children. These principles include Principles of individual differences, continuity, cephalocaudal and proximodistal, etc.
What are the four principles of growth and development?
The Major principles of growth and development are- principle of individual differences, the Principles of cephalocaudal and proximodistal, the Principle of interaction between Heredity and Environment, and the Principle of Integration
Why are the universal principles of growth and development important?
It allows us to predict how and when the growth and Development of certain characteristics show children at different stages. So teachers can Maximize the Growth and Development of children by knowing the universal principles of Growth and Development.