Phases of Teaching: Teaching is a complex task. For performing this task, systematic planning is needed, Teaching is to be considered in terms of various steps and the different steps constituting the process are called the phases of teaching.
Jackson thinks that if we are to obtain a complete description of the teaching activity, we must consider what the teacher does before and after his regular teaching in the class. Jackson divides the teaching act into three phases of teaching as shown below:
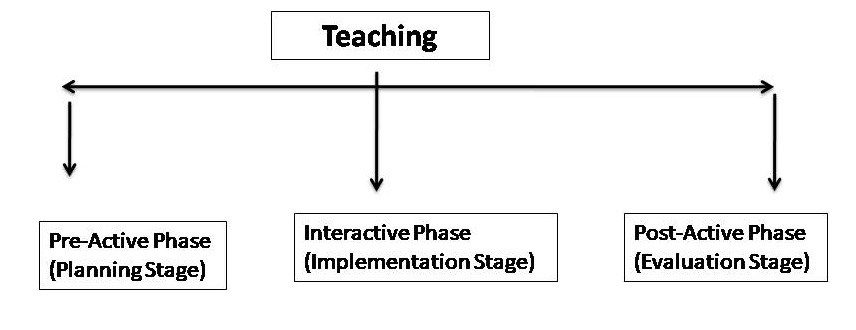
Phases of Teaching
The teaching process also can be explained as under:-
Pre-active Stage
It is the stage of planning for teaching that a teacher plan before going to the classroom to deal with students to teach. Before actual classroom teaching, a teacher has to perform many tasks.
These tasks include such as preparing lesson plans, arranging furniture and equipment within the classroom, manning papers, studying test reports, reading sections of a textbook and thinking about the aberrant behaviour of a particular student. These activities are very crucial to the teacher’s performance during the regular teaching session.
Pre-active behaviour is, more or less deliberative. The teacher at this stage hypothesizes about the possible outcome of his action. As the teacher decides what textbooks to use or how to group the children for reading or whether to notify students’ parents of their poor performance, his behaviour is at least analyzable.
Pre-active Stage of Teaching
The following operations or sub-stages are involved in pre-active stages of teaching-
1. Fixation of Goals
First of all the teacher determines the teaching objectives which are defined in the form of behavioural changes. Thus he ascertains the teaching objectives and what changes he requires in the pupils by achieving those objectives.
2. Decision making about the subject matter
After fixing the teaching objectives, the teacher makes the decision about the content which is to be presented before the pupils and as a result, he wants to bring the changes in the behaviour.
3. Arranging/Sequencing the elements of content for presentation
After making a decision regarding the contents to be presented to the pupils, the teacher arranges the elements of contents in a logical and psychological sequence, so that the arrangement of the contents elements may assist in the transfer of learning.
4. Decision making about the strategies of teaching
After sequencing the elements, the teacher makes a decision regarding the proper methods and strategies keeping in view the contents can be marked in the brain of the students very easily
5. Distribution of teaching strategies
In this stage, the teacher will decide how and when he will make use of which method and strategy during the classroom teaching. In other words, what type of question he will ask the pupils? When and where will he use the chart and maps? when will he deliver the lecture? when and how he will use the blackboard etc. All the activities should be determined by the teacher at the pre-active stage.
Interactive Stage.
This is actual classroom teaching. At this stage, the teacher uses a number of strategies for achieving the goals already set. In the interactive setting, the behaviour of the teacher is more or less spontaneous. Research suggests that things happen quickly during the teaching session. For example, the elementary teacher may change the focus of his concern as many as 1,000 times daily. Amid all this hustle and bustle the teacher often has little time to think.
Many teachers try to devote some time alone with individual students but the teacher-student dialogue is usually public rather than private. When a teacher is alone with a student, he is not faced with the problem of control and management that frequently absorbs a major portion of his energies in a group setting. There is a greater sense of physical and psychological intimacy between the teacher and the student during individual sessions than when the teacher is responding to the class as a group.
The task of keeping pupils involved may entail explanation, demonstration, definition, and other logical operations that have come to be thought of as the heart of teaching.
Operations at the Inter-active Stage
The inter-active stage of teaching involves the following:
1. Perception
Inter action process demands appropriate perceptions on the part of teachers as well as students with regards to classroom climate
2. Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis of the abilities and behaviour is very much essential for the appropriate interaction
3. Reaction process
For this purpose, the teacher has to take the right decision with regard to the selection and use of proper stimuli scheduled in the reinforcement and feedback devices and the development of suitable strategies suiting the need of the pupil’s teaching environment and teaching objectives.
Post-Active Stage
The post-active stage concerning evaluation provides necessary feedback to the teacher and the students in bringing desirable improvement in their performance. It is related to both teaching and learning.
The teacher analyses to what extent the students have grasped the material presented to them. It is in fact the assessment of the interactive process. It helps the teacher to teach things better in future. It also helps the students to learn things better. It enables the teacher to decide whether he should proceed with the new contents or re-teach what has already been taught
Operation at Post active stage
The following operations are involved at the post-active stage of teaching
1. Defining the exact decision of the behavioural changes
The teacher evaluates the expected behavioural changes with their actual behavioural changes during his teaching.
2. Selection of appropriate testing device
The teacher chooses certain suitable testing techniques and tools to measure the various desired dimensions of behaviour. The teacher should be reliable valid and objective in nature, cognitive and non-cognitive outcomes require a different types of testing devices
3. Changing and improving the strategies of teaching
The students testing results are also used to evaluate the effectiveness of instruction and teaching strategies. It may provide a basis for improving his teaching by re-orienting and changing strategies of teaching
Reference
- Principles, Methods & Techniques Of Teaching-By Sarita Aggarwal C/O Jca



