Gagne Conditions of Learning:
In 1956, The American Educational Psychologist Robert M. Gagne proposed a System of classifying different types of learning in terms of the degree of Complexity of the mental Process Involved.
Gagne identified eight basic types and arranged them in the hierarchy. According to Him, The Higher-order learning in this hierarchy builds upon the lower levels, requiring progressively greater amounts of previous learning for their success.
The lowest four orders tend to focus on the more behavioural aspects of learning while the highest four focus on the more cognitive aspects. The most complete description of Gagne’s classes of behaviour appears in his ‘The conditions of Learning. In this theory, Gagne distinguishes eight types of learning beginning with the simple forms and ending with the complex.
What Are Gagne Conditions of Learning?
Learning according to Gagne is-
- Learning is cumulative. Human intellectual development is the building of increasingly complex structures of Human Capabilities.
- Learning is the mechanism by which an individual becomes a competently functioning member of society
- Learning results in different kinds of human behaviours, i.e. different human capabilities, which are required both from the stimulation from the environment and the cognitive processing undertaken by the learners.
Gagne’s Taxonomy of Learning/ Hierarchy of Learning
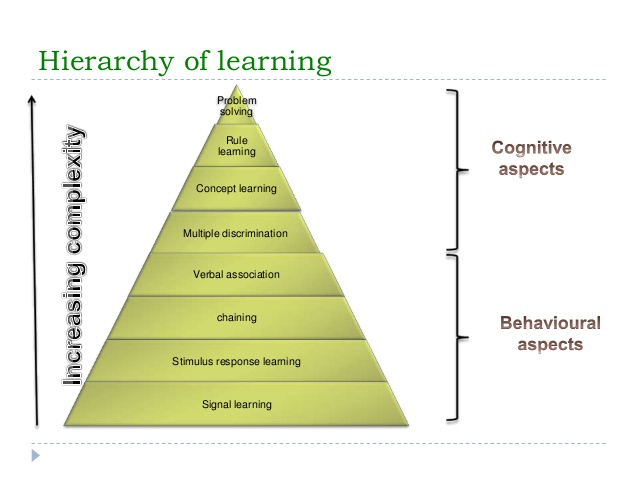
Robert Gagne gives eight types of the hierarchy of learning from simple to complex these are-
- Signal Learning
- Stimulus-Response Learning
- Chaining
- Verbal Association
- Discrimination Learning
- Concept Learning
- Rule learning
- Problem Solving
Signal Learning:
This is the simplest form of learning and consists essentially of the classical conditioning first described by the behavioural psychologist Pavlov. In this type of learning the animal or individual acquires a conditioned response to a given signal.
Example: When there is a Red Signal on Road, people stop their vehicles.
Stimulus-Response Learning
This is also known as operand Conditioning, which was originally developed by Skinner. Stimulus-response learning is all about getting a response to stimuli.
Example: When we place a plant in a Darkroom, It gets destroyed and when it is placed in a Sunlight it grows well.
Chaining
This is a more advanced form of learning in which the subjects develop the ability to connect two or more previously learned stimulus-response bonds into a linked sequence. It is the process whereby most complex psychomotor skills.
Example: When a child saw a Doll, She first represents it as a baby. She dresses up the Doll, does make for the Doll, the feeds the Doll.
Verbal Association
This form of chaining in which the links between the items being connected are verbal in nature. Verbal association is one of the key processes in the development of language skills. The simplest verbal association is the activity of naming an object which involves a chain of two links.
Example: When a child names an object “Ball”, it also says “Round Ball”, “ Black and White Ball”
Discrimination Learning
This involves developing the ability to make appropriate (different) responses to a series of similar stimuli that differ in a systematic way. This involves the development of the ability to differentiate an object, by its colour, shape, size etc.
Example: When seeing lots of cars on the road, differentiate the car by its name, Brand.
Concept Learning
This involves developing the ability to make a consistent response to different stimuli that forms a common class or category of some sort. It forms the basis of the ability to generalize, classify etc. In learning a concept we respond to stimuli in terms of abstract characteristics.
Example: While driving a car, one must start with clutch, and gear and then slowly release the clutch and raise the accelerator.
Rule learning
This is a very high-level cognitive process that involves being able to learn relationships between concepts and apply these relationships in different situations, including situations not previously encountered. In learning a rule we relate two or more concepts.
Example: When an air-filled Ball is kicked, it flies, rolls and revolves, it is a common rule. In this rule concepts such type of flying, rolling revolving etc are learned.
Problem Solving
This is the highest level of Cognitive process according to Gagne. It involves developing the ability to invent a complex rule, algorithm or procedure for the purpose of solving one particular problem and using the method to solve other problems of a similar nature.
Example: Teacher gives one maths problem in front of students and tells them to solve all the related problems from the chapter.



