National Curriculum Framework NCF-2005
| Education Policy | National Curriculum Framework |
| Published Year | 2005 |
| Published By | National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) |
| Chairman | Prof. Yash Pal |
| Language | Available in 22 Language |
| National Focus Group (NFG) | 21 National Focus Group |
| Total Committee members | 35 |
| Representative | Institute of Advance learning, NCERT Own Faculty, School Teacher, Non-Governmental Organisation |
| Previous NCF | Institute of Advance Learning, NCERT Own Faculty, School Teacher, Non-Governmental Organisation |
| Upcoming NCF | Institute of Advance Learning, NCERT Own Faculty, School Teacher, Non-Governmental Organisation |
The National Curriculum Framework (NCF)-2005 is open with a Quotation from Rabindranath Tagore’s essay “Civilization and Progress”. The NCF 2005 was published under the chairmanship of Prof. Yash Pal to Focus public attention on what should be taught to children and how.
The documents provide the framework for making syllabi, textbooks and teaching practices within the school education programs in India. The main purpose of developing NCF-2005 was to reduce the curriculum burden (Learning without Burden)
Needs of NCF-2005
- To remove ills of present school Education
- To promote “Learning without Burden”
- To improve ‘Creative thinking’ and discourage ‘Rote learning
- To clear the Education Purpose for Bright Future of Children
- To inculcate Holistic and Integrated approaches in School
- To remove Isolated Activities and Inflexibility of Schools.
Aims of Education according to NCF-2005
- Building a cohesive society
- Universalizing Elementary Education (UEE Development)
- Recognizing the interface between cognitive, Emotional and Action (physical) Development
- Empowering Teachers for Curriculum Development
- Respect for human dignity and Rights
- Independence of Thought and Action
- Development of Reasoning and Understanding
- Developing Secularism
- Concern for other well being
- Recognising India’s contribution to the World civilization
- Learner actively construct their own knowledge by connecting new ideas to existing, teacher should as facilitators
- Inclusive Environment in class for all
Guiding Principles of National Curriculum Framework (NCF)-2005
- Connecting Knowledge to life outside the school
- Ensuring that learning is shifted away from the rote method
- Enriching the curriculum to provide for the overall development of children rather than remaining textbook-centric
- Making examination more flexible and integrated into classroom life and
- Nurturing and overriding identity informed by caring concerns within the democratic polity of the country.
Main features of NCF-2005
Learning and Knowledge
- Primacy of Active Learner: Child-centered pedagogy means giving primacy to children’s experience, their voice and active participation
- Learners in context: Children will learn only in an atmosphere where they feel they are valued. Learning should be enjoyable and satisfaction
- Development & Learning: The curriculum should be holistic in nature to learn and develop an integrated approach. The physical growth of learners requires proper nutrition and physical exercise and it should be cognitive development so the students should have the capacity to make sense of self and world through action and language.
- The implication of curriculum and practice: Teaching for the construction of knowledge (Learners actively construct their knowledge), The value of interaction (Learning takes place through interaction with environment, nature, things and people), Designing Learning experience in such a way so that it can promote learning by doing and must have an approach for curriculum planning and critical pedagogy.
- Knowledge and understanding: Basic capabilities should be developed in children such as language forming and sustaining relationships, and capabilities for work and action. Knowledge and Practice-Craft such as weaving, and carpentry and occupations such as farming and visual arts these forms of knowledge are practical in nature. Forms of understanding, references, epistemic. Relational and significant understanding of the interconnection between different facts and concepts
- Some Development considerations: Acquiring a critical perspective on social reality and the natural environment through the senses provided by the subject matter. Connecting with locals in order to situate knowledge and realise its relevance and meaningfulness. Making connections across disciplines and bringing out the interrelatedness of knowledge. Realizing the fruitfulness and openness of enquiry and the provisional nature of truth. Encouraging questions and leaving space open for the pursuit of new questions. Developing the imagination and keeping imagination and fantasy alive
Curricular Areas, School Stage and Assessment
Language :
- NCF-2005 emphasis on the ‘Three Language Formula’
- In Hindi Speaking State-Mother Tongue or Regional Language is considered language-I, and Modern Indian Language or English is considered as Language-II, Another modern Indian Language can be considered as Language-III
- In a Non-Hindi Speaking State- Mother Tongue or regional Language is considered Lang-I, Hindi or English is considered Lang-II, Modern Indian language or English is considered Lang-III
- Multilingualism must be used as a resource for a Strategy
- Emphasis on Language Acquisition
- Literature can spur children’s own creativity
Mathematics:
- Children Learn to enjoy math’s rather than fear it
- Children pose and solve meaningful problems. Learning to solve maths is more important than the memorization of formula
- Children should understand the basic structure of Mathematics-Arithmetic, Algebra, Geometry, trigonometry and the basic concept of maths
- Teachers are expected to engage every child with the conviction that everyone can learn Maths
- Children should use maths as a part of their daily life experience.
- Maths Class emphasis on Mathematical content, process and Reasoning. Children should use Abstraction to perceive Relationships, to see structure to reason out things.
- The main goal of NCF is to Mathematizes the child’s thought process
- The Mathematics Curriculum should be ambitious and proficient. It should seek higher aims of teaching maths in School
Science
- Relate Science education to everyday life
- Nurturing the curiosity and cultivation of a scientific temper
- To promote rational thinking at the upper primary stage
- To teach science teachers should use the ‘Constructivist Approach
- The aims of Learning Science and its application, facts, and principles consistent with the stage of cognitive development
- Science curriculum be informed by a Historical perspective, enabling the learner to appreciate how concept evolves in time
- The curriculum should promote the value of Honesty, Objectivity, Cooperation and Freedom from fear and prejudice
Social Science
- To understand the Society in which the learner Lives
- To appreciate social values like equality, justice
- To develop a Scientific outlook in analyzing the problems faced by the society and Nation
- To develop skills for Social Interaction in Human Relationships
- To grow up as a responsible member of the society
- At Upper Primary Stage-Content like History, Geography, Political Science and Economics
- At Secondary Gender Justice, Issues related to SC/ST, Economic Aspects like Money, Banking, Commercial Issues and History.
Art Education:
- Students must be introduced to the rich traditions of the country. Music, dance and theatre contribute to the development of the self, both cognitive and social
Health and Physical Education:
- Provide a holistic understanding of fitness among children. To provide skills for dealing with psychosocial issues. Sports and games must added to the curriculum
Study of Peace
- Activity such as Listening with patience and purity of mind, concentration, cooperation of teamwork, appreciation of each other, Acceptance, and positive attitude should be developed in children through the peace-oriented curriculum
Work and Education:
- Work-related education is a component of the school curriculum, vocational Education, Craft Education, developed skills, values through work, work-related competencies
School and Classroom Environment
Physical Environment:
- The classroom should have enough space to be friendly and peaceful with lots of open space offering small nooks and corners, animals, flowers, plants and trees etc.
- The classroom should have adequate light and Drinking water facilities
- The classroom should equipped with furniture, equipment and books
Nurturing and Enabling Environment:
- Schools must be marked by the values of equality, social justice and respect for diversity, as well as the dignity and rights of children.
- Schools must be conscious of the importance of creating equitable classroom environments in which students are not subjected to being denied opportunities on the basis of their sex, caste, tribe, community etc
Active participation of children:
- Students should participate actively in community-level, cultural, and democratic activity
- A positive experience of democracy and democratic participation must be provided both within and outside the school
Discipline and Participatory Management:
- Education transaction has to shift from the benefactor (teacher) and the beneficiary (Students) to the motivator facilitator and learner, all of whom have rights and responsibilities in ensuring that educational transaction takes place
- Inculcating the value of self-discipline is important for the systematic pursuit of learning and the development of children’s interests and potential.
- Children should be encouraged to elect their own representatives to the children’s council.
Space for Parents and Community:
- Schools should provide community members in various programs and ask them to share their knowledge about the community and feedback on what needs to be improved it will help the teacher to design their curriculum
- In order to make the school environment supportive of children and to strengthen the relationship of the school with parents and the local-level committees and alumni association.
Curriculum Sites and Learning Resources:
- Tools, labs, Books, Alternative materials, Teaching Aids, Learning Resources, computer education, and Libraries should be available in the School for the all-round development of students.
Teacher Autonomy and Professional Independence:
- Teacher autonomy is essential for ensuring a learning environment that addresses children’s diverse needs.
- Relationships between the teacher and their heads and principals must be informed by equality and mutual respect and decision-making must be on the basis of dialogue and discussion
- There must be an encouraging atmosphere for the teacher
Time for Reflection and planning:
- On a daily basis (at least 45 minutes) review the day, make notes on children to follow up the next day, and organise materials for the next day’s lesson
- On a weekly basis ( at least two/three hours) to take stock of learning, work out details of activities and project proposed, and plan a group of lesson Units) for coming week
- On a month/term basis (minimum of one day) to review their own work, children learning
- At the beginning and end of the year two or three days each need to be allocated to evolve an annual plan for the school.
Systematic Reforms
Concern for Quality:
- NPE-2005 emphasises the improvement of the quality of education at different stages
- The tendency to confuse knowledge with information must be curbed. This tendency encourages the transfer of topics from higher to lower
- Treatment of children’s learning shifted from isolated to Holistic Development of children
- Curriculum choices have to be made with due regard to children’s context, ensuring the flexibility and diversity of the approach
- Educational technology should be used both for classroom teaching and teacher training
- The syllabus and Textbook design should be linked between the Primary, Upper Primary and Secondary levels in sequence order
Teacher Education for Curriculum Renewal:
- The curriculum renewal effort needs to be supported with a well-thought-out systematic program of in-service education and school-based teacher support
- Self-reflection needs to be acknowledged as a vital component of Teacher Education
- Mass training for teachers by using educational technology
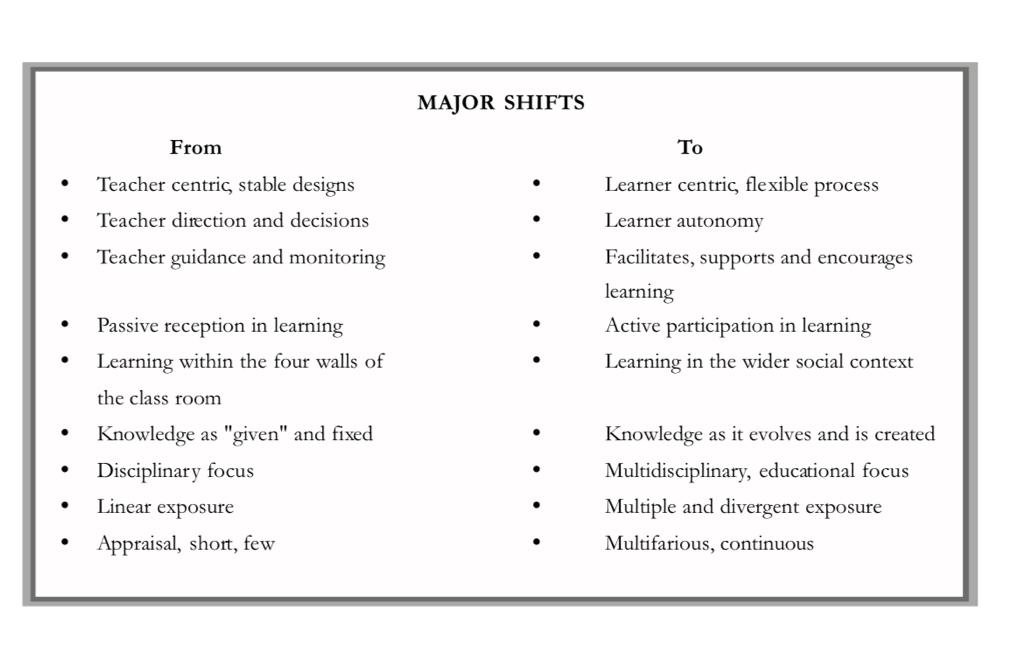
Examination Reforms:
- Examination at the end of Class X and Class XII should be reviewed with a view to replacing the text-based and Quiz type questioning which reduces the anxiety and stress of students
- Each school should implement the Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE), primarily for diagnosis, remediation and enhancement of learners.
- Flexibility in Assessment- Open book Exams and Exams without time limits are introduced as a pilot project. These innovations would have added the advantage of shifting the focus of exams from testing memory to testing higher-level competence such as interpretation, analysis and problem-solving skills
- Board Examination should be conducted at Class X optional if the children admitted in the same school for Higher Secondary do not need a board certificate to take an internal school exam instead
- There is a need to delink school leaving board examinations from competitive Entrance examination
Work Centered Education:
- Vocational education must be introduced into the school-level curriculum so that students can earn their livelihood by using the vocational skills
- Expansion of more ITI, Polytechnic, Technical School, Krishi Vigyan Kendra’s, Rural Development Agencies etc
- Career counselling programs should be introduced that enable children to systematically plan their movement toward their future vocation or livelihoods.
Innovation in ideas and practices:
- The writing of the textbook should be in such a way that it includes Academic and research inputs, understanding of children’s developmental levels, effective skills of communication and designing
- Individual teachers should be transacting the curriculum according to the needs of students
- Teachers should encourage the students to innovate their new ideas and use them in practice
- The technology should be used such as ICT in the teaching and learning process
New Partnership:
- NCF-2005 emphasises increasing the involvement of Non-Governmental organizations and civil society groups in education.
- NGO has played a major role in creating innovative models of schooling, training of teacher, development of textbook and curricular materials, community mobilization and advocacy
- The civil society group’s role is to give education a visible public space and facilitate the emergence of discouragement on the child’s right to education
- The role and functions of SCERTs need to include providing support not only in purely academic areas but psychological aspects as well
- There is also a need for institutional linkages between universities and institutions such as SCERTs and DIETs to strengthen their academic programs of teacher education and in-service training as well as to develop their research capacities
Conclusion
NCF-2005 is a comprehensive Framework for School Education-Learning Without Burden
- It emphasizes the child-centered approach focusing on the Holistic Development of Students
- It encourages a flexible, learner-centric curriculum that promotes critical thinking and creativity
- It emphasises the introduction of vocational education at the School level to the Higher Secondary level
- NCF-2005 aims to foster a joyful and stress-free learning environment, reducing rote memorization and exam-oriented teaching
- It encourages to adoption of Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE)